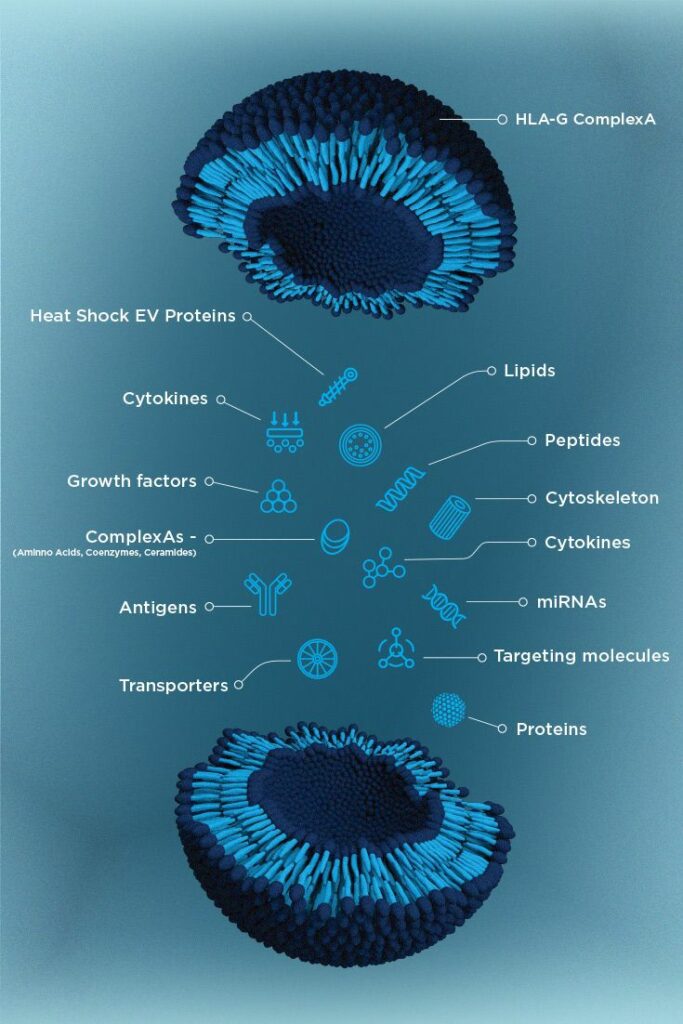
Exosomes are tiny extracellular vesicles that have captured the attention of scientists and healthcare professionals for their significant roles in cell communication and potential therapeutic applications. Found in many biological fluids, such as blood, urine, and saliva, exosomes are pivotal in numerous physiological and pathological processes.
What are Exosomes?
Exosomes are small membrane-bound vesicles, typically ranging from 30 to 150 nanometers in diameter. They originate from the endosomal compartment in cells and are released when multivesicular bodies fuse with the plasma membrane. Despite their minuscule size, they pack a punch in cellular communication, carrying lipids, proteins, and genetic materials like RNA between cells.
Functions and Importance
The primary function of exosomes is intercellular communication. They facilitate the transfer of molecules between cells, influencing various biological processes. Exosomes play vital roles in immune responses, neuronal communication, and tumor progression.
Recent research highlights their potential in precision medicine, as circulating exosomes can provide critical insights into the state of health or disease in an individual. Thus, they serve as promising biomarkers for early detection and monitoring of diseases, including cancers and neurodegenerative disorders.
Exosomes in Therapeutics
The therapeutic application of exosomes is a burgeoning field. Due to their natural ability to transfer therapeutic molecules across biological barriers, they are being engineered as delivery systems for drugs, proteins, and nucleic acids. This approach aims to enhance the specificity and efficacy of treatments, potentially leading to breakthroughs in managing chronic diseases.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the promising potential, exosome research and application face several challenges, such as standardizing isolation and characterization techniques. Ensuring scalability for clinical applications is another hurdle researchers are actively working to overcome.
Looking ahead, the field of exosome research is expanding with a robust pipeline of clinical trials focusing on various diseases. Continued advancements in understanding these nano-sized communicators promise exciting developments in diagnostics and therapeutics.
In conclusion, exosomes are ushering in a new era in biomedical sciences with their ability to act as tiny yet powerful messengers. As research progresses, they could redefine how we diagnose and treat diseases, affirming their status as tiny messengers with big potential.
